Six Sigma: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
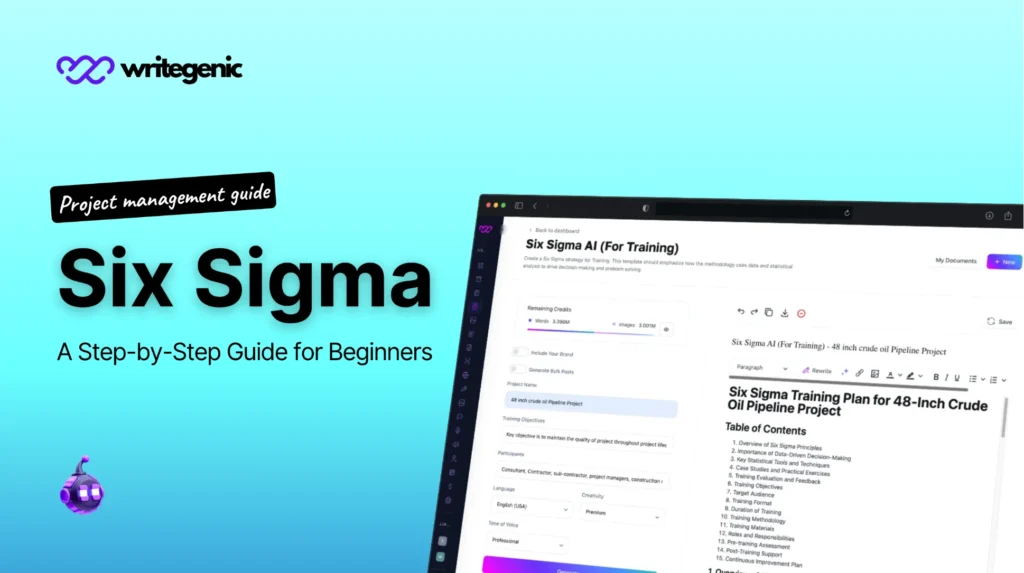
Six Sigma has become one of the most important strategies that organizations find necessary to achieve competence in the current competitive business world through enhanced efficiency, reduced wastages and enhanced performance. A systematic method of process improvement qualifies as one of the most effective strategies of attaining these objectives. This strategy is optimized to streamline work processes, reduce the errors, and guarantee high-quality outcomes, which makes it an essential tool of businesses operating in a variety of areas.
In this guide for beginners, we will take you through the basics on process optimization, how it is used in business processes, the extent of certifications, the sequential approach to projects, and how to monitor and overcome issues with this methodology.
Table of Contents
What Is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is an analytical activity of measured data that tries to enhance the quality of activities by focusing on defects and their reduction. It was developed by Motorola in the 1980s and popularized by General Electric, the purpose of Sigma is to eliminate variation and make a process more controlled to approach perfection.
Six Sigma is a term that is used to denote the statistical notion of three point four or fewer defects per million chances. It is based on quality management techniques and statistics to promote continual improvement.
Role of Six Sigma in Business Process Optimization
The role of Sigma in the business process optimization is transformative. It assists in helping organizations:
- Reduce waste and process inefficiencies
- Improve product or service quality
- Increase customer satisfaction
- Enhance decision-making through data
- Save costs and maximize profitability
It might be related to parts manufacturing, health care, finance, or IT, but this Sigma can make business processes leaner and achieve the hard, business benefits.
Example: An example is a logistics company that employed Sigma by investigating the root cause analysis and optimised their supply chain network, delivering packages to customers much faster resulting in a high rate of customer satisfaction.
Understanding Six Sigma Levels
Six Sigma is a hierarchical method of learning and implementing the methodology, symbolized by “belts”:
- White Belt: Basic understanding of Six Sigma principles; supports teams on projects.
- Yellow Belt: Participates in projects and understands how Six Sigma is implemented.
- Green Belt: Leads small-scale projects; works under the supervision of Black Belts.
- Black Belt: Expert in Six Sigma; manages large projects and mentors Green Belts.
- Master Black Belt: Strategic leader who trains and coaches Black Belts.
These levels are not only an indication of expertise, but also a defining element of capacity and responsibility of people in Sigma groups.
Key Phases of a Six Sigma Project (DMAIC)
The backbone of any Six Sigma project is the DMAIC framework, which stands for:
Define
Determine the problem, objectives and the scope of the project. Get to know the business needs and priorities of the customers.
Measure
Gather information, determine base measures, and determine current performance of processes. Appropriate measure of the extent of the problem is very essential.
Analyze
Find fundamental causes of the issue by means of tools of statistics. Find out the source of variation and defects.
Improve
Identify, test, and put in place solutions towards removing root causes. Fine-tune innovative, but data-informed optimizations.
Control
Monitor performance so that improvement can be maintained. Put in place control systems and documentation to be successful long term.
Every stage applies its tools and procedures to guarantee detailed evaluation and long-lasting outcomes.
Six Sigma Problem Solving Techniques
Effective Six Sigma problem solving relies on several proven tools:
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa): Identifies potential causes of a problem.
- 5 Whys Analysis: Drills down to the root cause through iterative questioning.
- Pareto Chart: Highlights the most significant factors contributing to a problem.
- Control Charts: Monitors process behavior over time.
Using these tools allows teams to focus on data-backed insights rather than assumptions.
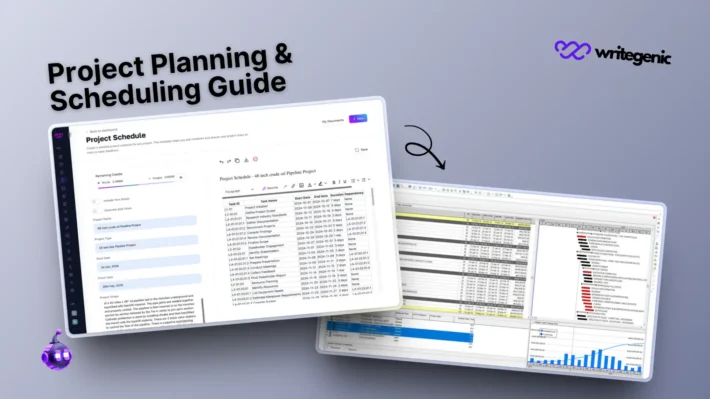
Six Sigma Project Tracking and Management
Tracking a Six Sigma project is essential for success. Project tracking involves:
- Defining clear milestones and timelines
- Using tools like dashboards, Gantt charts, or Six Sigma software
- Holding regular meetings and updates
- Documenting all actions, changes, and results
Six Sigma project tracking ensures transparency, accountability, and alignment with business goals.
Getting Started: How Beginners Can Apply Six Sigma
If you’re new to Six Sigma, here are the steps to start:
Learn the basics
Start with a White or Yellow Belt certification. These are often free or low-cost and provide foundational knowledge.
Choose a project
Identify a small, manageable process you can improve. This could be reducing email response times or streamlining a routine report.
Apply DMAIC
Use the five-phase process to guide your improvement efforts.
Use tools
Learn to apply statistical tools, root cause analysis, and visual management techniques.
Get support
Join a process improvement team or seek mentorship from experienced professionals—collaboration accelerates learning.
Many organizations support continuous improvement initiatives by sponsoring training and pilot projects. Take advantage of online courses, books, forums, and case studies to deepen your understanding.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Those new to the methodology often encounter challenges such as:
- Resistance to change: Overcome this with stakeholder education and involvement.
- Data limitations: Start small and focus on what’s measurable.
- Lack of training: Invest in foundational certifications.
- Misalignment with goals: Ensure that projects are tied to business objectives.
Overcoming these challenges requires persistence, communication, and support from leadership.
Conclusion
This methodology is more than just a set of tools—it’s a mindset focused on excellence and continuous improvement. For beginners, understanding the different levels, following the DMAIC structure, and practicing effective problem-solving and project tracking are key to success.
Whether you’re aiming to reduce waste, solve process inefficiencies, or drive better outcomes, this proven framework can guide you there. Now is the perfect time to start your journey toward process excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What industries benefit the most from process improvement techniques?
Process optimization is commonly used in manufacturing, healthcare, finance, logistics, IT, and service-based industries to improve efficiency and reduce defects.
What is the difference between general process improvement and Lean approaches?
Traditional methods focus on reducing variation and defects, while Lean emphasizes eliminating waste. The combination results in faster and more efficient improvement.
How long does it take to get certified in process improvement methodologies?
Entry-level courses can take a few hours or days. More advanced certifications may take several weeks to a few months, depending on the program.