Lean Methodology Plan: Fundamentals Explained for you
The Lean Methodology Plan is crucial to success in business in the current rapidly changing environment achieved by adaptability, pace, and customer-focused businesses. Rather than basing plans on large budgets or thick documents, lean planning is practical, adaptable, and fast with the value delivery. This philosophy is built on efficiency and the ability to continue improving, which helps organisations to reduce wastages, optimise work processes, and be competitive in dynamic markets.
Whether you are starting a startup organization, building a product, or running internal operations, lean practice provides a practical direction that makes you fast-moving and excellent. This guide will take you through all the basics you need to know including; lean planning, lean business model and the strategic thinking that brings it all together.
Table of Contents
What Is Lean Methodology?
Lean methodology is a well-organized method of the creation of maximum customer value with minimum waste. Originated in the Toyota Production System in the middle of the 20 th century, now it is a gold standard in such industries as manufacturing, software development, startups, and project management.
Contrary to the conventional methods of operation involving excessive planning, future wastage, and long-term strategy, lean approach adheres to the following priorities:
- Customer feedback
- Iterative development
- Constant process improvement
- Efficient use of resources
This makes it an adjustable and expandable planning methodology that can be applied in small teams as well as in big enterprises.
The Role of Lean Planning
A heart of lean methodology is lean planning. It concentrates on fast decision and modification of plans with reference to real statistics and feedback rather than to hypothetical multi year projections.
Why Lean Planning Matters:
The conventional business plans are usually tens of pages long, and the authors can spend months on them, only to find themselves making changes a few weeks later at the time of execution. Conversely, lean planning is:
- Fast to create
- Flexible to adjust
- Focused on key drivers of success
In traditional planning, you are expected to know it all beforehand but in lean planning you agree to live with uncertainty and incorporate the ability into the process. This is a perfect planning methodology of startups, agile teams, and product developers.
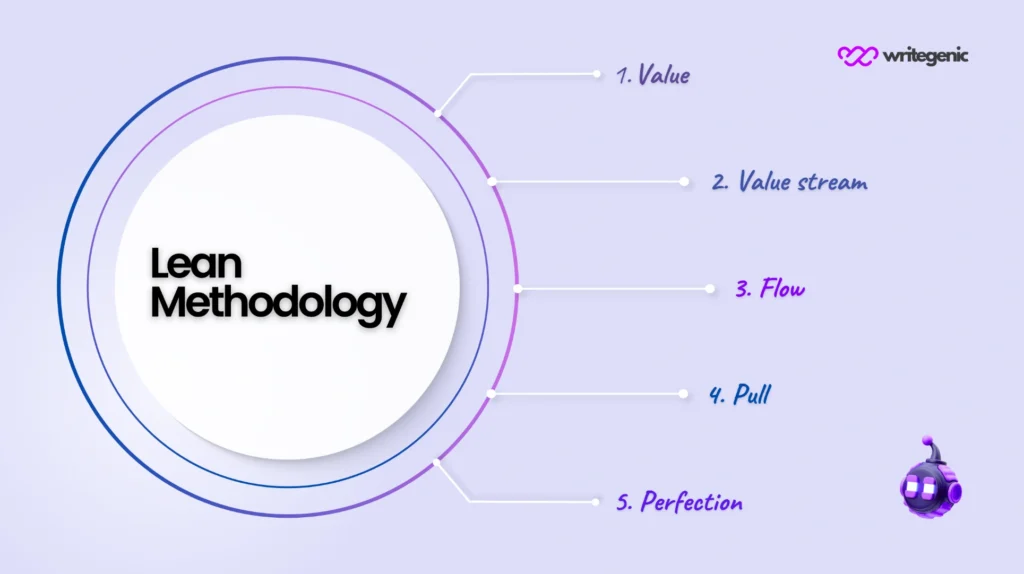
Core Principles Behind Lean Strategy
Lean strategy is simply not about reducing the fat, but miming smarter systems. Lean philosophy is based on five principles that are essential to it:
1. Eliminate Waste (Muda)
Anything that fails to add value to the customer is regarded as waste. By eliminating it the resources are released.
2. Build Quality Into the Process
Lean promotes designing processes that are error-proof as opposed to inspection.
3. Create Knowledge
Real user feedback, hypothesis testing, and data-driven strategy development and adaptation are important elements of a lean mindset.
4. Optimize Flow
The flowing through of the value, that is free of breakages, is synonymous with lean success whether in a product development pipeline, or supply chain.
5. Pursue Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Lean can never be complete. The continuous improvement is incorporated into the process so that the growth becomes sustainable.
By adhering your lean strategy to these principles, your firm is going to gain speed and precision of its activities.
How to Create a Lean Business Plan
A lean business plan is simplified and nimble in the form of a traditional business plan. It cuts off the excess fat and concentrates strictly on the knowledge you should test, develop, and expand.
Key Components of a Lean Business Plan:
- Vision Statement – What would you hope to achieve in the long run?
- Problem Statement – What are you solving as a pain point for the customers?
- Solution – What product/service will you provide?
- Customer Segments – What are your perfect users?
- Key Metrics – What will you consider success?
- Revenue Model – What is your business model?
- Channels – How are you going to communicate to your customers?
- Cost Structure – What are your main expenses?
- Milestones – What are your short term goals of execution?
The lean business plan, unlike the traditional business plans, which require loads of documentation and forecasts, enables you to make quick adjustments based on customer review and market conditions.
Lean Business Model: What Makes It Different?
The lean methodology is helped by the lean business model that is oriented toward value creation and rapid adaptation. Lean Canvas is one of the most popular tools that was employed in this model; it is a one page visual strategizing tool to simplify thinking.
Lean Canvas Elements:
- Problem
- Customer segments
- Unique value proposition
- Solution
- Key metrics
- Revenue streams
- Cost structure
- Channels
- Unfair advantage
Rather than completing endless spreadsheets and paragraphs, you can visualize your business. This promotes more rapid decision-making, testing, and resource allocation improvement.
As a startup or a small team, the lean approach to business is usually the perfect solution you need- you can remain tight and focused on solving concrete problems rather than on the pursuit of vanity metrics and hierarchy.
Examples of Lean Methodology in Practice
Lean methodology is not only a theory; it is a tried and tested exposure that many of the most innovative global companies have adopted.
- Dropbox: They built a very simple explainer video as opposed to developing a complete product. The feedback given by the users affirmed the idea, sparing them both time and money.
- Toyota: Creator of lean, Toyota cut wastage of production and came up with a high standard of products with the use of lean concepts such as just-in-time inventory and continuous improvement.
- Airbnb: Lean principles helped Airbnb to quickly test various ideas and refined their model until they were able to find a winning group.
These are some of the instances that demonstrate how combining lean strategy with lean planning cuts business innovation time, ease adaptation, and enables streamlined scaling.
Creating Your Own Lean Methodology Plan
When you decide it is time to go lean, this is how to initiate your lean methodology plan:
Start With a Lean Business Plan
Write your problem, solution, customer and metrics in a one-page style.
Use the Lean Canvas
Enter all the fields to have a clear and fast look at your business strategy.
Set Short-Term Milestones
Set objectives that you are able to achieve during 1-4 weeks to maintain momentum and enable quick iteration.
Validate Your Assumptions
Put your product or your idea to test. Listen to their feedback, to pivot or to get better.
Measure Progress Continuously
By monitoring your main metrics, you will know what is effective and what has to be altered.
Encourage Team Involvement
Lean is most effective when the entire team is connected and ready to make the data-based decisions.
These steps would help you to develop a lean plan that is responsive, intelligent and result-oriented.
Conclusion
Lean Methodology Plan is not a mere simplification strategy but an attitude transformation. It provokes companies to be critical, fast and become the best constantly. The lean methodology provides the knowledge and practices to enable you to build a new product, start a business, or optimize your operations no matter your industry and have a chance to succeed in a complex and competitive world.
With lean planning, a lean business plan and a lean business model based on value in mind you are able to cut the waste, prioritize what is important and provide actual value to your customers in a record time.
FAQs about Lean Methodology Plan
How does a Lean Methodology Plan differ from traditional planning?
A Lean Methodology Plan is not as demanding in terms of extensive forecasting and rigorous documentation like traditional planning, but lighter and one that revolves around the concept of iterative development. It gives opportunities to make changes quickly relying on real facts and feedback and minimizing the chance of making costly errors.
Who should use a Lean Methodology Plan?
Lean Methodology Plan is more suitable in situations and organizations where the characteristics of the environment are speedy or unpredictable, where startups, small businesses, product development teams, and project managers are working. Its application is particularly helpful when fast decision making and repeated testing are required.
Can large organizations implement a Lean Methodology Plan?
Well, yes, large organizations should realize that using a Lean Methodology Plan they could apply its principles to particular teams, departments or projects. Although the lean way was developed as a solution in environments dominated by smaller organizations being more agile, the main principles, such as optimization of waste and enhanced flow are never-ending across different settings.
How does a Lean Methodology Plan support innovation?
A Lean Methodology Plan establishes an atmosphere conducive to innovation by placing a premium on continuous experimentation, customer validation, and quick turnaround, which are essential to innovation. The teams are enabled to work more rapidly and iterate ideas because quick testing of ideas, failure learning, and improvement of real life solutions each are undertaken.